“After” Approaches Emphasize Stakeholders, Systems Perspective and “Third Way†Thinking
By Kathleen M. Hosfeld (with Jenny Mish)
Thousands of sustainability oriented startups are creating game-changing innovations in products, services, industry partnerships, supply chain management and more as they seek to integrate values of social justice and environmental stewardship into their business practices.
As startups, they represent one part of the new sustainability economy. The other side is existing “traditional†businesses seeking to integrate sustainability into both the culture and business processes at the same time. For the former group, the challenge is making it work without a roadmap. For the latter, it’s creating change in systems that seem to have worked “just fine†before sustainability came along.
Until recently, there hasn’t been much recognition of the role that marketing can play in furthering sustainability. Superficial promotional claims of green characteristics of products and services in the 1980s — what’s now known as “green washing†— actually created something of setback for the sustainability movement. Today, marketing functions – such as product design or supply chain transparency– that are critical to success may not – in some organizations – have been seen as part of marketing.
As more organizations have succeeded in integrating sustainability, marketing researchers and people in the field are noticing an emerging picture of what sustainability oriented marketing looks like.
Jenny Mish, a doctoral candidate in marketing at the University of Utah, and I saw the outlines of this emerging picture in data she gathered as a part of her doctoral work. She completed a study of “Exemplary Triple Bottom Line Companies,†in the summer of 2007. She identified several themes emerging as characteristic of marketing in sustainability oriented companies:
- They view their situations through a complex, systems perspective – highlighting interrelationships of components and stakeholders
- They take a long-term triple bottom line approach – finding third-way solutions instead of creating trade-offs between goals
- They engage a broad array of stakeholders
- They integrate full-cycle product (or service) costs into their understanding of what creates value and relevance for customers
- They emphasize relational, trust-based communications and sales approaches
Many of these organizations express these characteristics as “authenticity†– saying they reflect their values (“This is who we areâ€). Comparing Jenny’s interview data with my consulting experience in the field, we have created a series of polarity diagrams that demonstrate the contrast between marketing that is not at all sustainability oriented and marketing that fully embraces sustainability. This comparison begins to create some guidelines for those companies who want to practice sustainability oriented marketing. This offers a picture of what they might or should be striving for.
Marketing “Before†And “After†Sustainability
This series of three diagrams contrasts a simplistic, single-bottom line oriented approach to marketing with a complex, triple-bottom-line approach to sustainability marketing:
- It’s important to stress that the two ends of the spectrum do not exist in pure forms. The right side of each diagram actually represents a collage of sustainability oriented marketing“best practices.â€
- We suspect that lower profitability on the left side is the result of a more limited marketing skill set that coincides with a simplistic approach.

Figure 1. Managerial Orientation
To make a transition to sustainability oriented marketing, the values and perspectives of sustainability must be reflected at the top. Although some studies show that sustainability efforts can “start from the middle,†– marketers need agreement and support from other managers to make sustainability a
priority. Without this, the pressure on marketers to drive only short-term sales targets will create either/or situations where marketers are forced to choose between profit and sustainability goals. Figure 1 contrasts the managerial orientation of the two ends of the spectrum.

Figure 2. Relationships with Stakeholders
What we see in organizations that make this transition is that at some point the expectation of the marketing function flips. The extreme polarity on the left represents marketing as strictly the job of “selling.†(Again it’s important to stress that the two ends of the spectrum are not descriptions of actual businesses, but rather extreme points of view.) At some point, exemplary organizations pursuing a triple bottom line demonstrate a perspective that marketing is the stewardship of relationships in the context of assumed reciprocity. They certainly don’t remove the sales imperative from the table. However,marketing is charged with accomplishing the goals of the organization for sales, profit and mission by providing superior benefit and relevance to not just customers alone but also to other stakeholders.
Figure 2 depicts the key relationships of which marketers become stewards in a sustainability oriented setting.
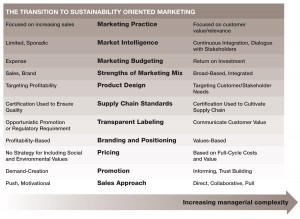
Figure 3. How Stakeholder Relationships are Stewarded
The final figure demonstrates how various aspects of marketing practice – from budgeting to research to pricing to promotion – change in character when the purpose of marketing shifts from “selling stuff†to “stewarding relationships.â€
What we notice in this chart is that a much higher degree of marketing sophistication is required to practice marketing from a stewardship perspective. For example, whereas many organizations do not have a defined approach to pricing – for example, they price intuitively based on what the market will
bear – sustainability oriented organizations must develop the capacity to measure the full cycle cost of a product or service and base their pricing accordingly.
The approach to market intelligence or customer research also changes. On the left, consumers are studied so that their needs can be addressed in sales and promotion. Sustainability oriented marketers, on the other hand, seek to foster ongoing dialogue with customers and other stakeholders. It’s considered a continuous conversation, where even “co-creation†may take place when that is valuable on both sides.
Another characteristic that was noted from Jenny’s study is that in sustainability oriented marketing, marketing functions and expertise are dispersed throughout the organization. Marketing – or rather stewardship of stakeholder relationships – is “everyone’s job.†It’s important to note that many companies who haven’t consciously adopted sustainability principles yet practice a high degree of ethics and have high standards for authenticity and trust in customer and other stakeholder relationships. We sense that these companies are well placed on the continuum toward the right hand side of the polarity diagrams even if the ideas of social justice and environmental stewardship are not yet part of their corporate consciousness.
What Does All This Mean?
For those companies who are already embracing sustainability, this comparison of “before†and “after†may identify new areas to deepen their practice. For those who are just getting started, leaders in organizations may want to take note of the following:
- Marketers need to be supported in integrating sustainability and its values into their practices. They may need to be challenged to hold financial, social and environmental goals simultaneously. Or they may need assurance from the top that the company is serious about measuring success by all three.
- Marketers may also need to be challenged to think and act from a systems perspective. They need to be supported and trained to look for “third way†solutions rather than seeing multiple bottom lines as areas for trade-offs. In the end this may pay off in innovation. The ability to hold multiple objectives simultaneously and search for the “third way†has led, in the past, to new products and services, as well as more efficient manufacturing and delivery systems.
- The overall marketing skill of the organization must be enhanced. Marketers should receive professional development in areas where they may lack experience. A sense of “stewardship of relationships†should be fostered in the company as a whole so that sustainability oriented marketing becomes “everyone’s job.â€
A “printer friendly” version of this article, with larger graphics, is available here.



